2,500-Year-Old Siberian Ice Mummy: A Study Of Ancient Tattoos
Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
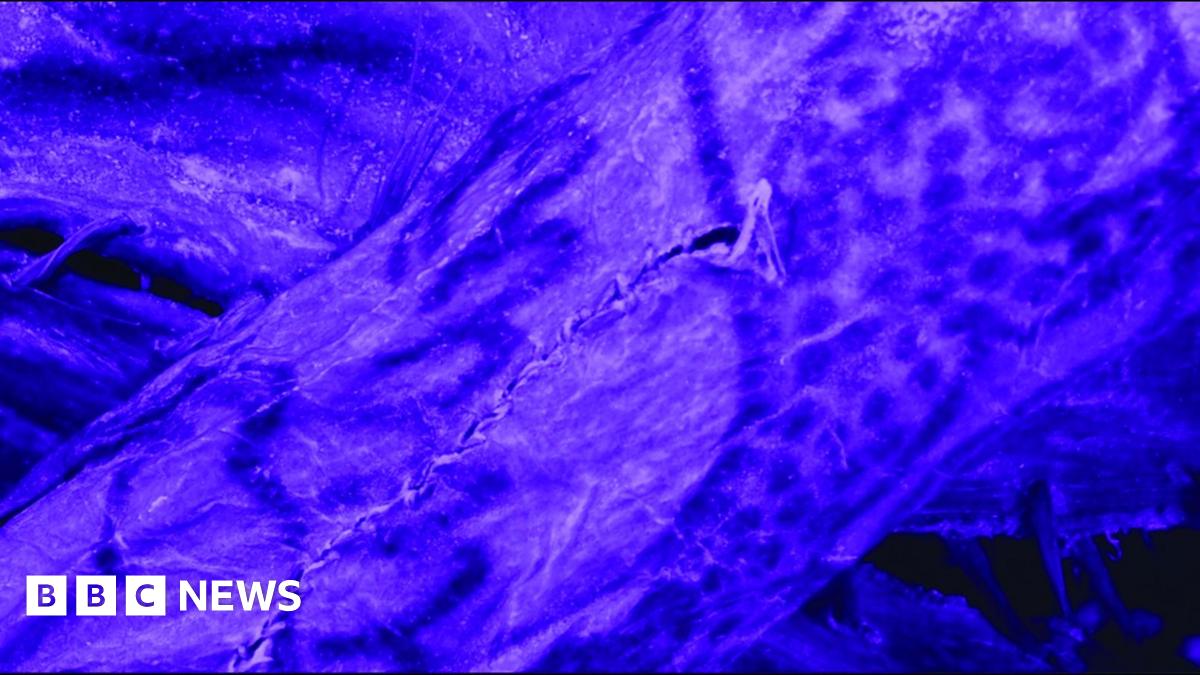
2,500-Year-Old Siberian Ice Mummy Reveals Stunning Ancient Tattoo Art
The frozen wastes of Siberia have yielded another incredible secret: a remarkably preserved ice mummy adorned with intricate tattoos, offering a rare glimpse into the body art practices of the Pazyryk culture over 2,500 years ago. This discovery, detailed in a recent study published in [Insert Journal Name and Link Here], is revolutionizing our understanding of ancient Siberian societies and their artistic expressions.
The mummy, a male believed to be a high-status individual based on his burial goods and the complexity of his tattoos, was unearthed in the Altai Mountains. The exceptional preservation conditions, thanks to the permafrost, have allowed researchers to meticulously document the tattoos, revealing a sophisticated level of artistry previously unseen in this region.
Deciphering the Designs: A Window into Pazyryk Culture
The tattoos, executed with a technique likely involving a needle and ink made from natural pigments, are primarily located on the upper body. They feature a series of animal motifs, including:
- Deer: Often associated with shamanistic practices and spiritual journeys in many ancient cultures.
- Horses: Symbolic of power, wealth, and status within the Pazyryk society. Their depiction could indicate the mummy's role as a warrior or leader.
- Geometric patterns: These abstract designs may represent clan affiliations, spiritual beliefs, or social status. Further research is needed to fully interpret their meaning.
The precision and detail of the tattoos suggest a skilled practitioner, possibly a shaman or a member of a specialized artistic class. This level of artistry points to a more complex and nuanced social structure than previously imagined.
Advanced Techniques and Preservation: A Scientific Marvel
The remarkable preservation of the tattoos, despite the passage of millennia, is a testament to the power of permafrost and the careful excavation techniques employed by the research team. Scientists used high-resolution imaging techniques, including [mention specific techniques used, e.g., multispectral imaging], to analyze the tattoos without damaging the delicate remains.
This non-invasive approach not only allows for the detailed study of the tattoos but also preserves the mummy for future research. The findings provide valuable insights into the materials used in ancient tattooing, the techniques employed, and the potential health implications of such practices.
Connecting the Dots: Ancient Tattoos and Siberian History
This discovery adds to a growing body of evidence showcasing the rich cultural heritage of the Pazyryk people. Previous archaeological finds in the Altai Mountains have revealed elaborate burial mounds, exquisite textiles, and evidence of sophisticated metalworking. The tattoos provide a powerful visual connection to these earlier discoveries, enriching our understanding of this fascinating ancient civilization.
The study of this 2,500-year-old Siberian ice mummy and its tattoos provides a unique opportunity to unravel the mysteries of ancient Siberian societies. Further research is underway to analyze the pigments used, potentially uncovering insights into the resources and trade networks of the Pazyryk people. This incredible find emphasizes the importance of ongoing archaeological research and the preservation of our cultural heritage.
Call to Action: Learn more about the ongoing research on ancient Siberian cultures by visiting [link to relevant museum or research institution website]. Support archaeological preservation efforts by donating to [link to relevant charity or organization].

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on 2,500-Year-Old Siberian Ice Mummy: A Study Of Ancient Tattoos. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Pattinson Not The Next Batman Gunn Sets The Record Straight On Dcu Plans
Aug 02, 2025
Pattinson Not The Next Batman Gunn Sets The Record Straight On Dcu Plans
Aug 02, 2025 -
 Tech Earnings Bonanza Apple Exceeds Forecasts Amazon Underwhelms Reddits Strong Showing
Aug 02, 2025
Tech Earnings Bonanza Apple Exceeds Forecasts Amazon Underwhelms Reddits Strong Showing
Aug 02, 2025 -
 No Gubernatorial Run For Harris California 2026 Election Update
Aug 02, 2025
No Gubernatorial Run For Harris California 2026 Election Update
Aug 02, 2025 -
 30 Million Fraud Oyster Bay Resident Pleads Guilty Admitting To Offering Political Connections
Aug 02, 2025
30 Million Fraud Oyster Bay Resident Pleads Guilty Admitting To Offering Political Connections
Aug 02, 2025 -
 Palestinian State Recognition Impacts On Geopolitics And International Law
Aug 02, 2025
Palestinian State Recognition Impacts On Geopolitics And International Law
Aug 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 X Qc Vs Kai Cenat Who Reigns Supreme In Streaming Net Worth
Aug 03, 2025
X Qc Vs Kai Cenat Who Reigns Supreme In Streaming Net Worth
Aug 03, 2025 -
 Backlash Against Bbc Master Chef Faces Cancellation After Judge Sackings
Aug 03, 2025
Backlash Against Bbc Master Chef Faces Cancellation After Judge Sackings
Aug 03, 2025 -
 Mr Beasts Challenge Cenat Vs X Qcs Streaming Empire Compared
Aug 03, 2025
Mr Beasts Challenge Cenat Vs X Qcs Streaming Empire Compared
Aug 03, 2025 -
 New Policy Only Working Class Individuals Eligible For Civil Service Internships
Aug 03, 2025
New Policy Only Working Class Individuals Eligible For Civil Service Internships
Aug 03, 2025 -
 Public Outrage Prompts Master Chef Review Bbc Responds To Judge Controversy
Aug 03, 2025
Public Outrage Prompts Master Chef Review Bbc Responds To Judge Controversy
Aug 03, 2025
