Could Lithium Deficiency Contribute To The Development Of Alzheimer's?
Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Could Lithium Deficiency Contribute to the Development of Alzheimer's? A Growing Area of Research
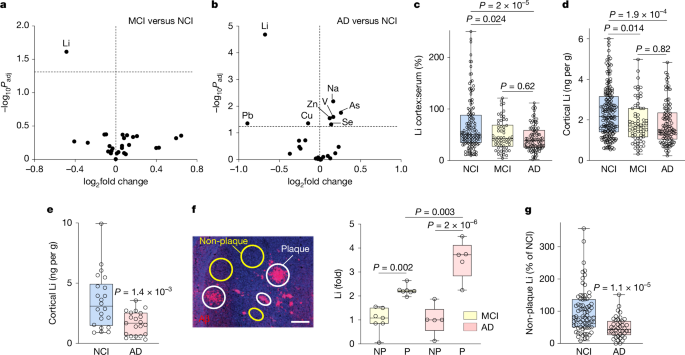
Alzheimer's disease, a devastating neurodegenerative disorder affecting millions worldwide, remains a significant public health challenge. While the exact causes are still under investigation, a growing body of research points towards a potential link between lithium deficiency and the increased risk of developing this debilitating condition. This article explores the emerging evidence suggesting that inadequate lithium levels might play a role in Alzheimer's pathogenesis.
The Intriguing Role of Lithium:
Lithium, a naturally occurring element, is primarily known for its use in treating bipolar disorder. However, its therapeutic effects extend beyond mood stabilization. Studies have demonstrated lithium's neuroprotective properties, suggesting it could potentially protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. This protective effect may be linked to several mechanisms:
- Reduced Neuroinflammation: Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease. Lithium has been shown to reduce neuroinflammation, potentially slowing the progression of the disease.
- Improved Tau Protein Regulation: Tau protein tangles are a characteristic feature of Alzheimer's pathology. Research suggests that lithium may influence tau protein regulation, preventing the formation of these harmful tangles.
- Enhanced Synaptic Plasticity: Lithium's impact on synaptic plasticity – the brain's ability to adapt and learn – may help maintain cognitive function and prevent cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer's.
- Protection against Amyloid Beta Plaque Formation: The accumulation of amyloid beta plaques is another key feature of Alzheimer's. Some research indicates that lithium may inhibit amyloid beta aggregation.
Evidence Linking Lithium Deficiency to Alzheimer's Risk:
While more research is needed to establish a definitive causal link, several studies provide intriguing clues:
- Geographical Variations: Areas with lower lithium levels in drinking water have been associated with higher rates of Alzheimer's disease. This correlation, however, does not prove causation and requires further investigation controlling for other confounding factors.
- Observational Studies: Observational studies have shown that individuals with lower blood lithium levels may have a higher risk of developing Alzheimer's. These studies, however, cannot definitively determine causality, only suggesting a possible association.
- Preclinical Research: Animal models have demonstrated that lithium supplementation can offer neuroprotection against Alzheimer's-like pathology. This preclinical data supports the potential benefits of lithium, but needs translation to human studies.
The Importance of Further Research:
The current evidence is compelling but not conclusive. Further research is crucial to fully understand the role of lithium in Alzheimer's pathogenesis. This includes:
- Larger, well-designed epidemiological studies: These studies are necessary to confirm the observed associations between lithium levels and Alzheimer's risk.
- Clinical trials: Randomized controlled trials are needed to determine whether lithium supplementation can prevent or delay the onset of Alzheimer's disease in humans. Such trials must carefully consider dosage, duration, and potential side effects.
- Mechanistic studies: More research is needed to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which lithium exerts its neuroprotective effects.
Conclusion:
The possibility that lithium deficiency contributes to the development of Alzheimer's disease represents a promising area of research. While the current evidence is suggestive rather than definitive, the potential for lithium to play a preventative or therapeutic role warrants further investigation. This research could lead to novel strategies for preventing or treating this devastating condition. Stay informed about advancements in Alzheimer's research and consult with your healthcare provider for any concerns related to cognitive health. Further research is vital to solidify these findings and translate them into effective clinical interventions. The future of Alzheimer’s treatment may very well depend on understanding the intricate relationship between trace minerals like lithium and neurological health.

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Could Lithium Deficiency Contribute To The Development Of Alzheimer's?. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Governor Kristi Noem Faces The Wrath Of South Park
Aug 09, 2025
Governor Kristi Noem Faces The Wrath Of South Park
Aug 09, 2025 -
 Cincinnati 2025 Kartal Garcias Ongoing Contributions
Aug 09, 2025
Cincinnati 2025 Kartal Garcias Ongoing Contributions
Aug 09, 2025 -
 Chat Gpts Gpt 5 Rollout A User Backlash Against Model Replacements
Aug 09, 2025
Chat Gpts Gpt 5 Rollout A User Backlash Against Model Replacements
Aug 09, 2025 -
 Inter Milan Pre Season Friendlies Ticket Availability
Aug 09, 2025
Inter Milan Pre Season Friendlies Ticket Availability
Aug 09, 2025 -
 Inter Milan Pre Season Tickets For Sale Limited Availability
Aug 09, 2025
Inter Milan Pre Season Tickets For Sale Limited Availability
Aug 09, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Jaxson Darts Preseason Debut Best Plays And Highlights From Week 1
Aug 10, 2025
Jaxson Darts Preseason Debut Best Plays And Highlights From Week 1
Aug 10, 2025 -
 Hall Of Fame Candidate Billy Howton Packers Star And Nflpa Founder Dead At 95
Aug 10, 2025
Hall Of Fame Candidate Billy Howton Packers Star And Nflpa Founder Dead At 95
Aug 10, 2025 -
 Apollo 13s Jim Lovell A Life In Space And A Nations Tribute
Aug 10, 2025
Apollo 13s Jim Lovell A Life In Space And A Nations Tribute
Aug 10, 2025 -
 Nicola Sturgeons Memoir Arrest Detailed As Worst Day Of My Life
Aug 10, 2025
Nicola Sturgeons Memoir Arrest Detailed As Worst Day Of My Life
Aug 10, 2025 -
 Mike Huckabee Weighs In Starmers Leadership And Wwii Hypothetical
Aug 10, 2025
Mike Huckabee Weighs In Starmers Leadership And Wwii Hypothetical
Aug 10, 2025
