Dinosaur Die-Off: New Clues From A Canadian Pachyrhinosaurus Site

Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Dinosaur Die-Off: New Clues from a Canadian Pachyrhinosaurus Site
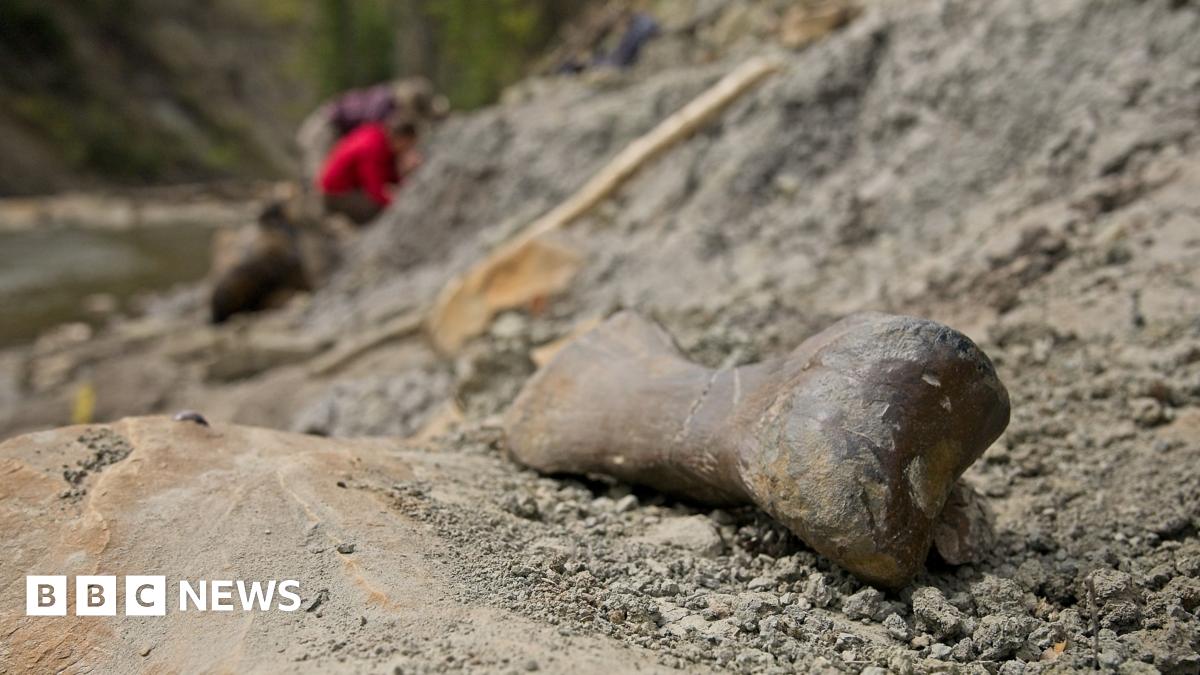
A groundbreaking discovery in Canada sheds new light on the mass extinction event that wiped out the dinosaurs 66 million years ago. A remarkably preserved Pachyrhinosaurus bonebed in Alberta is providing paleontologists with unprecedented insights into the final days of these majestic creatures. The findings, published in Nature Communications, challenge existing theories and offer a more nuanced understanding of the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction.
The site, located in the Wapiti Formation, boasts an exceptionally high concentration of Pachyrhinosaurus fossils, many exhibiting signs of trauma and disease. This isn't just another dinosaur graveyard; it's a snapshot of a population struggling to survive in the face of catastrophic environmental change. The sheer density of fossils suggests a sudden, catastrophic event, rather than a gradual decline.
<h3>A Closer Look at the Pachyrhinosaurus Findings</h3>
The researchers, a team from the University of Alberta and the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology, meticulously examined hundreds of Pachyrhinosaurus bones. Their analysis revealed several key findings:
- High levels of bone pathologies: Many bones showed evidence of infections, fractures, and other injuries, suggesting a weakened population vulnerable to disease and predation. This points to a stressful environment impacting the dinosaurs' overall health before the final extinction event.
- Evidence of rapid burial: The way the fossils are preserved indicates a rapid burial event, consistent with a sudden catastrophic occurrence, such as a massive flood or earthquake. This supports the theory of a sudden, rather than gradual, extinction.
- Age diversity: The bonebed contains fossils from Pachyrhinosaurus of various ages, suggesting that the event impacted all age groups equally. This contradicts some theories that only specific age groups were disproportionately affected.
<h3>Challenging Existing Theories of Dinosaur Extinction</h3>
The Canadian Pachyrhinosaurus site adds a crucial piece to the puzzle of the K-Pg extinction. While the impact of the Chicxulub asteroid remains the leading hypothesis, this discovery underscores the complexity of the event. It suggests that environmental stressors, possibly exacerbated by volcanic activity in the Deccan Traps, significantly weakened dinosaur populations prior to the asteroid impact, making them more susceptible to extinction.
<h3>What This Means for Our Understanding of Mass Extinction</h3>
This research highlights the importance of studying fossil assemblages to understand the dynamics of mass extinction events. The Pachyrhinosaurus bonebed isn't merely a collection of bones; it's a powerful narrative of a population's struggle for survival in the face of overwhelming odds. This discovery reinforces the idea that multiple factors, working in concert, likely contributed to the demise of the dinosaurs. Further research on similar sites around the globe is crucial to refine our understanding of this pivotal moment in Earth's history.
<h3>Further Research and Future Implications</h3>
The research team plans to continue their analysis of the Wapiti Formation bonebed, employing advanced techniques like isotopic analysis to gain a more detailed picture of the environment in which these dinosaurs lived and died. This ongoing work will undoubtedly continue to shed light on the K-Pg extinction event and our understanding of mass extinction in general. The implications extend beyond dinosaurs, offering valuable insights into how ecosystems respond to catastrophic events and the vulnerability of species to environmental change. This is particularly relevant in our current era of climate change and biodiversity loss.
Call to Action: Learn more about paleontology and the ongoing research into the dinosaur extinction by visiting the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology website or exploring resources from the University of Alberta. Staying informed about these discoveries helps us better understand our planet's past and protect its future.

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Dinosaur Die-Off: New Clues From A Canadian Pachyrhinosaurus Site. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Investor Confidence In Ethereum Soars 200 M Fund Investment Following Pectra
May 21, 2025
Investor Confidence In Ethereum Soars 200 M Fund Investment Following Pectra
May 21, 2025 -
 Balis Tourism Crisis A Call For International Collaboration On Safety And Behavior
May 21, 2025
Balis Tourism Crisis A Call For International Collaboration On Safety And Behavior
May 21, 2025 -
 Exclusive Interview Jamie Lee Curtis On Maintaining Her Bond With Lindsay Lohan
May 21, 2025
Exclusive Interview Jamie Lee Curtis On Maintaining Her Bond With Lindsay Lohan
May 21, 2025 -
 Report Reveals Lufthansa Flight Flew Unaided For 10 Minutes After Co Pilot Collapsed
May 21, 2025
Report Reveals Lufthansa Flight Flew Unaided For 10 Minutes After Co Pilot Collapsed
May 21, 2025 -
 Devastating St Louis Tornado Cleanup And Recovery Efforts Begin
May 21, 2025
Devastating St Louis Tornado Cleanup And Recovery Efforts Begin
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Jeremy Bowen Reports Growing International Condemnation Of Israels Gaza Actions
May 21, 2025
Jeremy Bowen Reports Growing International Condemnation Of Israels Gaza Actions
May 21, 2025 -
 Urgent Warning Severe Storm Risk In North Carolina Tonight
May 21, 2025
Urgent Warning Severe Storm Risk In North Carolina Tonight
May 21, 2025 -
 Jeremy Bowen On Gaza Will International Demands End The Offensive
May 21, 2025
Jeremy Bowen On Gaza Will International Demands End The Offensive
May 21, 2025 -
 Top Rated Sunscreens For 2025 Safe For Family And You
May 21, 2025
Top Rated Sunscreens For 2025 Safe For Family And You
May 21, 2025 -
 Ellen De Generes Returns To Social Media A Heartfelt Message For Fans
May 21, 2025
Ellen De Generes Returns To Social Media A Heartfelt Message For Fans
May 21, 2025
