Man-Eater Screwworm: Assessing The Risk And Implementing Solutions

Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Man-Eater Screwworm: Assessing the Risk and Implementing Solutions
The dreaded man-eater screwworm, Cochliomyia hominivorax, is a parasitic fly capable of causing severe myiasis – infestation of living tissue – in both humans and animals. While eradicated from the continental United States since the 1960s thanks to the Sterile Insect Technique (SIT), its potential for resurgence presents a significant risk, demanding continuous monitoring and proactive solutions. This article delves into the current risk assessment, preventative measures, and effective control strategies for this dangerous parasite.
Understanding the Threat: A History of the Man-Eater Screwworm
The man-eater screwworm's life cycle begins with the female fly laying its eggs in open wounds or orifices of warm-blooded animals, including humans. These eggs hatch into larvae, which burrow into the flesh, feeding on living tissue and causing significant pain, infection, and potentially death if left untreated. The larvae mature, drop off the host, pupate, and emerge as adult flies, continuing the cycle. Historically, screwworm infestations caused significant livestock losses and posed a considerable threat to public health. The successful eradication program in the US involved releasing millions of sterile male flies, thus preventing reproduction.
Current Risk Assessment: Where Are We Now?
While eradicated from the continental US, the man-eater screwworm remains prevalent in Central and South America. This proximity, coupled with the potential for accidental introduction through livestock movement or human travel, necessitates ongoing vigilance. The risk is considered low but not negligible, making continuous surveillance and rapid response capabilities crucial. Outbreaks in the past have demonstrated the speed at which this parasite can spread and the devastating impact it can have on both animal health and human well-being.
Preventative Measures: Protecting Humans and Livestock
Preventing screwworm infestations is paramount. Key preventative measures include:
- Wound Care: Prompt and thorough cleaning and treatment of any open wounds on both humans and animals are essential to prevent egg-laying.
- Livestock Management: Regular inspection of livestock for wounds and prompt veterinary care can minimize infestation risks. Maintaining clean and sanitary conditions in animal housing is also critical.
- Border Control: Strict border controls and inspections of imported livestock and animal products help to prevent the introduction of screwworm flies.
Control Strategies: Effective Responses to Outbreaks
Should an outbreak occur, effective control strategies are vital to contain its spread. The most effective method remains the Sterile Insect Technique (SIT):
- Sterile Insect Technique (SIT): This involves mass-rearing and sterilizing male flies, which then mate with wild females, resulting in infertile eggs and a reduction in the population. This method has proven highly successful in previous eradication efforts.
- Chemical Control: Insecticides can be used as a supplementary control measure, particularly in localized areas. However, this approach needs to be carefully managed to minimize environmental impact.
- Surgical Intervention: Infested wounds require immediate surgical removal of larvae and treatment of infection.
The Future of Screwworm Control: Research and Collaboration
Continued research into improving SIT effectiveness, developing more environmentally friendly insecticides, and enhancing surveillance technologies are crucial for maintaining the current eradication status in the US and preventing future outbreaks. International collaboration is essential for effective control and eradication programs, particularly in areas where the screwworm remains endemic.
Conclusion: Staying Vigilant Against a Persistent Threat
The man-eater screwworm, despite its eradication from the continental US, remains a significant threat. Maintaining a robust surveillance system, implementing preventative measures, and employing effective control strategies, including the SIT, are essential for protecting both human and animal health. Continuous research and international cooperation are vital to ensuring the long-term control of this dangerous parasite. Staying informed and proactive is crucial in mitigating the risk posed by this persistent threat.

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Man-Eater Screwworm: Assessing The Risk And Implementing Solutions. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
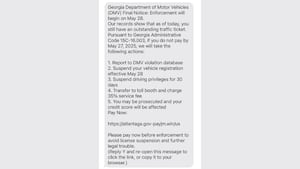 Fake Text Message From Ga Department Of Driver Services How To Spot The Scam
May 28, 2025
Fake Text Message From Ga Department Of Driver Services How To Spot The Scam
May 28, 2025 -
 American Life Vs German Life Why One Expat Returned Home Disappointed
May 28, 2025
American Life Vs German Life Why One Expat Returned Home Disappointed
May 28, 2025 -
 Red Carpet Reveal Alexandra Daddarios See Through Gown At Dior
May 28, 2025
Red Carpet Reveal Alexandra Daddarios See Through Gown At Dior
May 28, 2025 -
 The Giannis Antetokounmpo Trade Market Assessing Realistic Contenders
May 28, 2025
The Giannis Antetokounmpo Trade Market Assessing Realistic Contenders
May 28, 2025 -
 600 Billion Pledge A New Chapter In Billionaire Philanthropy
May 28, 2025
600 Billion Pledge A New Chapter In Billionaire Philanthropy
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 French Media Censorship Macrons Marital Ad Disappears
May 30, 2025
French Media Censorship Macrons Marital Ad Disappears
May 30, 2025 -
 Musician Rick Derringer Dead At 77 His Collaborations And Impact
May 30, 2025
Musician Rick Derringer Dead At 77 His Collaborations And Impact
May 30, 2025 -
 High Profile Jailbreaks Fuel Renewed Debate On Us Prison Security
May 30, 2025
High Profile Jailbreaks Fuel Renewed Debate On Us Prison Security
May 30, 2025 -
 Tesco Shoppers Mock Self Checkout Surveillance
May 30, 2025
Tesco Shoppers Mock Self Checkout Surveillance
May 30, 2025 -
 In Memoriam George Strait Remembers His Hero Victim Of North Texas House Fire
May 30, 2025
In Memoriam George Strait Remembers His Hero Victim Of North Texas House Fire
May 30, 2025
