Rising Beef Prices: The Primary Driver Of Year-High Food Inflation

Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Rising Beef Prices: The Primary Driver of Year-High Food Inflation
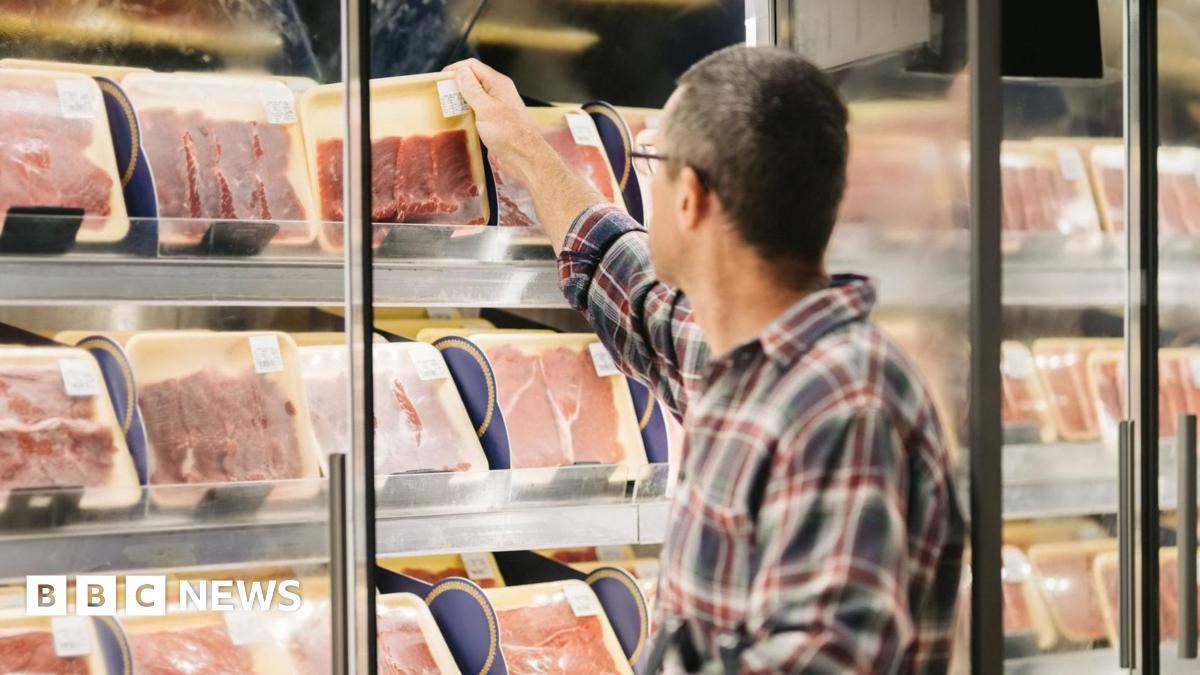
Food prices are soaring, hitting year-high levels and impacting household budgets across the nation. While various factors contribute to this inflationary surge, the dramatic increase in beef prices stands out as a key culprit. This isn't just about the cost of a steak; it's a significant economic issue affecting everything from grocery bills to restaurant menus.
The Perfect Storm: A Convergence of Factors
Several interconnected factors have created a perfect storm driving up beef prices. Understanding these intricacies is crucial to grasping the broader implications of this food inflation crisis.
1. Drought and Reduced Cattle Supply: Severe drought conditions in key cattle-producing regions have significantly reduced pastureland and feed availability. This has led to ranchers culling herds, resulting in a smaller supply of cattle ready for market. Less supply inevitably translates to higher prices, a fundamental principle of economics. [Link to USDA Drought Monitor].
2. Increased Feed Costs: The drought also directly impacts the cost of feed for cattle. Higher prices for corn, hay, and other feedstuffs are directly passed on to consumers in the form of more expensive beef. This cascading effect underscores the interconnectedness of agricultural markets.
3. Rising Transportation and Labor Costs: Like many other industries, the beef industry is grappling with increased transportation and labor costs. These added expenses are factored into the final price consumers pay at the grocery store or restaurant. This is particularly relevant given the significant logistical challenges associated with transporting livestock and processed beef.
4. Increased Demand: Despite higher prices, demand for beef remains relatively strong. This robust demand, coupled with reduced supply, further exacerbates the price increases. Consumer preferences and eating habits play a significant role in this dynamic.
5. Processing Plant Issues: Challenges within the meat processing industry, including labor shortages and occasional plant closures, have also contributed to supply chain disruptions and higher prices. These bottlenecks ripple throughout the entire system, impacting the timely and efficient processing and distribution of beef.
The Impact on Consumers and the Economy:
The impact of these rising beef prices is far-reaching:
- Increased Grocery Bills: Families are feeling the pinch as the cost of staples like ground beef and steaks climb. This disproportionately affects lower-income households, further widening the economic gap.
- Restaurant Menu Inflation: Restaurants are forced to raise prices to maintain profitability, impacting consumer spending in the dining sector.
- Inflationary Pressure: The rise in beef prices contributes to overall food inflation, which in turn fuels broader economic inflation. This has major implications for monetary policy and overall economic stability.
What Lies Ahead?
Predicting future beef prices is challenging, as it depends on several unpredictable factors, including weather patterns and global economic conditions. However, experts suggest that prices are unlikely to decrease significantly in the near term.
Looking for Alternatives?
Consumers looking to mitigate the impact of rising beef prices can explore alternative protein sources, such as poultry, pork, fish, or plant-based options. [Link to article on alternative protein sources]. This offers a chance to diversify diets and potentially reduce food costs.
Conclusion:
The skyrocketing price of beef is a critical component of the current food inflation crisis. Understanding the interwoven factors driving this increase – from drought and feed costs to processing plant issues and robust demand – is essential for policymakers, businesses, and consumers alike. The long-term implications remain uncertain, but navigating this challenge requires a multifaceted approach addressing supply chain inefficiencies, climate change resilience, and consumer behavior.

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Rising Beef Prices: The Primary Driver Of Year-High Food Inflation. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Thames Water Faces Largest Ever Fine 122 7 Million Penalty
May 29, 2025
Thames Water Faces Largest Ever Fine 122 7 Million Penalty
May 29, 2025 -
 600 Billion Pledge The Future Of Billionaire Philanthropy And Its Challenges
May 29, 2025
600 Billion Pledge The Future Of Billionaire Philanthropy And Its Challenges
May 29, 2025 -
 A Critical Look At Harvard Addressing Its Issues While Preferring It To Trumps Leadership
May 29, 2025
A Critical Look At Harvard Addressing Its Issues While Preferring It To Trumps Leadership
May 29, 2025 -
 Preventing Early Heart Attacks Lessons From Partner Losses
May 29, 2025
Preventing Early Heart Attacks Lessons From Partner Losses
May 29, 2025 -
 Increased Security Measures Following Recent High Profile Jailbreaks In The Us
May 29, 2025
Increased Security Measures Following Recent High Profile Jailbreaks In The Us
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 De Chambeau Explains Why Public Courses Present Unexpected Challenges
Jul 17, 2025
De Chambeau Explains Why Public Courses Present Unexpected Challenges
Jul 17, 2025 -
 Historic High For Tsmc Q2 Profits Up 60
Jul 17, 2025
Historic High For Tsmc Q2 Profits Up 60
Jul 17, 2025 -
 Los Cabos Open Basavareddy Claims Victory Alvarez Advances
Jul 17, 2025
Los Cabos Open Basavareddy Claims Victory Alvarez Advances
Jul 17, 2025 -
 Heat And High Stakes Tennis The Los Cabos Open Begins
Jul 17, 2025
Heat And High Stakes Tennis The Los Cabos Open Begins
Jul 17, 2025 -
 Englands Farming Crisis Hundreds Of Farms Accused Of Illegal Water Extraction
Jul 17, 2025
Englands Farming Crisis Hundreds Of Farms Accused Of Illegal Water Extraction
Jul 17, 2025
