Rising Tick Populations Fuel Lyme Disease Concerns In The Northeast

Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Rising Tick Populations Fuel Lyme Disease Concerns in the Northeast
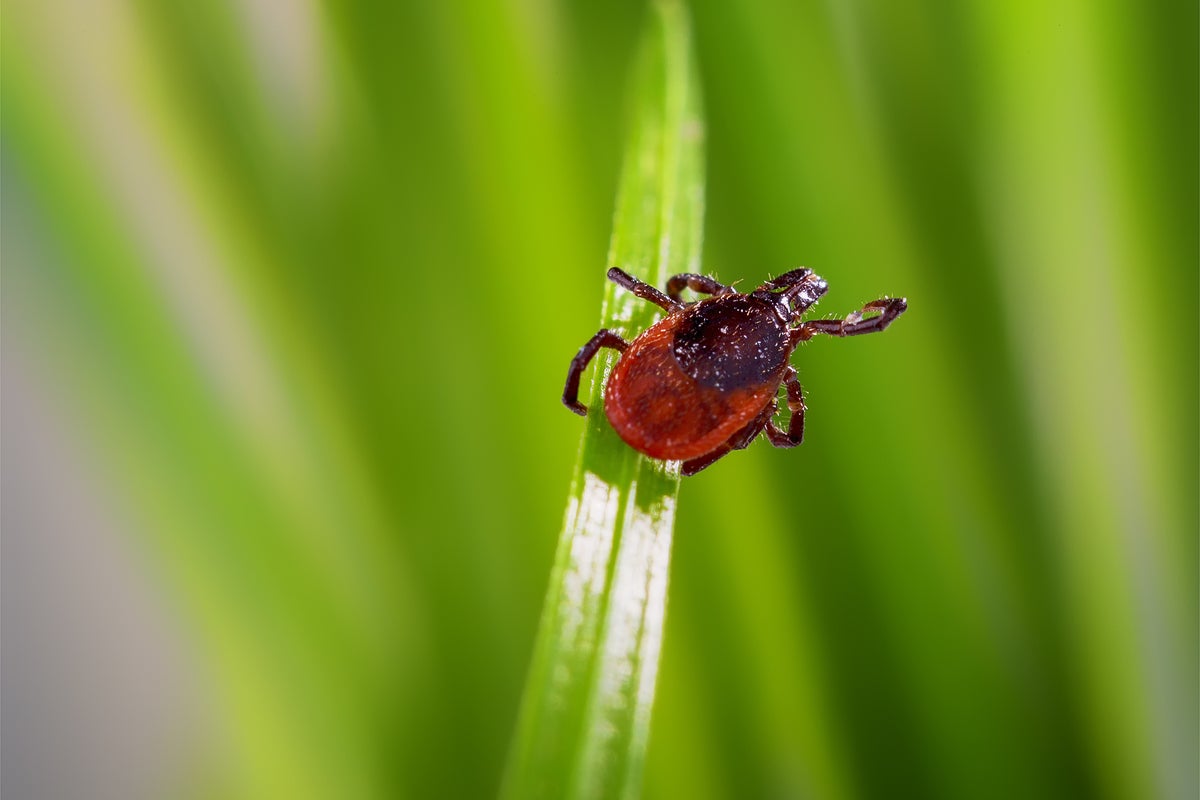
Lyme disease cases are on the rise in the Northeastern United States, driven by a significant increase in tick populations. Warmer winters and expanding deer populations, key hosts for blacklegged ticks (also known as deer ticks), are contributing factors to this alarming trend. This poses a significant public health concern, impacting both residents and visitors to the region.
The Northeast, encompassing states like Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania, has long been a hotspot for Lyme disease. However, recent reports indicate a sharp escalation in both tick numbers and confirmed Lyme cases, prompting renewed calls for preventative measures and increased public awareness.
The Tick Factor: Understanding the Rise in Populations
Several interconnected factors are fueling the surge in tick populations:
-
Milder Winters: Warmer temperatures throughout the winter months mean fewer ticks are killed off by the cold, allowing them to survive and reproduce at higher rates. This increased survival rate translates directly into a larger tick population the following spring and summer.
-
Expanding Deer Population: White-tailed deer are essential hosts for blacklegged ticks. An increase in deer populations, often due to habitat changes and successful breeding seasons, provides more breeding grounds and sustenance for ticks, leading to a rapid population expansion.
-
Changing Habitats: Human encroachment into wooded areas and suburban sprawl bring people into closer contact with tick-infested habitats, increasing the risk of tick bites and subsequent Lyme disease infection.
Lyme Disease: Symptoms and Prevention
Lyme disease, caused by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi, is transmitted through the bite of an infected blacklegged tick. Early symptoms can be subtle and often mimic other illnesses, making diagnosis challenging. These include:
- A characteristic "bullseye" rash: Not everyone develops this rash, but its presence is a strong indicator of Lyme disease.
- Fever, chills, and fatigue: These flu-like symptoms are common in the early stages.
- Muscle and joint aches: Pain in the muscles and joints can be significant.
- Headache and neck stiffness: These symptoms can be debilitating.
Prevention is crucial. Here are some key steps to reduce your risk:
- Wear long sleeves and pants: Protect exposed skin when venturing into wooded or grassy areas.
- Use insect repellent: Apply EPA-registered repellents containing DEET, picaridin, IR3535, or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
- Perform tick checks: Carefully examine yourself and your pets for ticks after spending time outdoors. Remove any attached ticks promptly using tweezers.
- Maintain your lawn: Keep your lawn mowed short and clear brush and leaf litter to reduce tick habitats.
Seeking Medical Attention
If you suspect you may have Lyme disease, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics are essential for preventing serious long-term complications. Delaying treatment can lead to more severe symptoms affecting the joints, heart, and nervous system.
Looking Ahead: The Need for Continued Research and Public Health Initiatives
The increasing prevalence of Lyme disease in the Northeast demands a multi-pronged approach. This includes further research into tick biology and disease transmission, improved diagnostic tools, public health campaigns to increase awareness, and the implementation of effective tick control strategies. Collaboration between researchers, healthcare professionals, and public health agencies is vital to combat this growing public health challenge. Staying informed and taking proactive steps to protect yourself and your family is crucial in mitigating the risk of Lyme disease. For more information on Lyme disease prevention and treatment, visit the .

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Rising Tick Populations Fuel Lyme Disease Concerns In The Northeast. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Idf Strikes Yemeni Ports And Galaxy Leader Ship Details Of The Israeli Operation
Jul 08, 2025
Idf Strikes Yemeni Ports And Galaxy Leader Ship Details Of The Israeli Operation
Jul 08, 2025 -
 Falling Gravestone Claims Young Life In Rawtenstall
Jul 08, 2025
Falling Gravestone Claims Young Life In Rawtenstall
Jul 08, 2025 -
 Rebuilding Cancer Care A Foundation For The Future
Jul 08, 2025
Rebuilding Cancer Care A Foundation For The Future
Jul 08, 2025 -
 Perpetual Equity Investment Announces Revised Nta Backing
Jul 08, 2025
Perpetual Equity Investment Announces Revised Nta Backing
Jul 08, 2025 -
 Marine Veteran Battles Ice Detention Of Breastfeeding Wife
Jul 08, 2025
Marine Veteran Battles Ice Detention Of Breastfeeding Wife
Jul 08, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Investigation Are Texas Childrens Camps Built In Floodplains
Jul 08, 2025
Investigation Are Texas Childrens Camps Built In Floodplains
Jul 08, 2025 -
 Why Air Canada And Aeroplan Are Top Choices For Us Flyers
Jul 08, 2025
Why Air Canada And Aeroplan Are Top Choices For Us Flyers
Jul 08, 2025 -
 Relief For Australian Mortgages Analysis Of The Next Rate Cut
Jul 08, 2025
Relief For Australian Mortgages Analysis Of The Next Rate Cut
Jul 08, 2025 -
 Guest Leaves Baby Shower After Infertility Joke A Story Of Hurt Feelings
Jul 08, 2025
Guest Leaves Baby Shower After Infertility Joke A Story Of Hurt Feelings
Jul 08, 2025 -
 Cnn Mounted Volunteers Aid In Locating Missing Individuals
Jul 08, 2025
Cnn Mounted Volunteers Aid In Locating Missing Individuals
Jul 08, 2025
